Data Integrity in the Personalized Medicine Journey
Personalized medicine, such as mRNA-based cancer vaccines, has the potential to revolutionize medicine. Data integrity (DI) is crucial for trustworthy manufacturing.
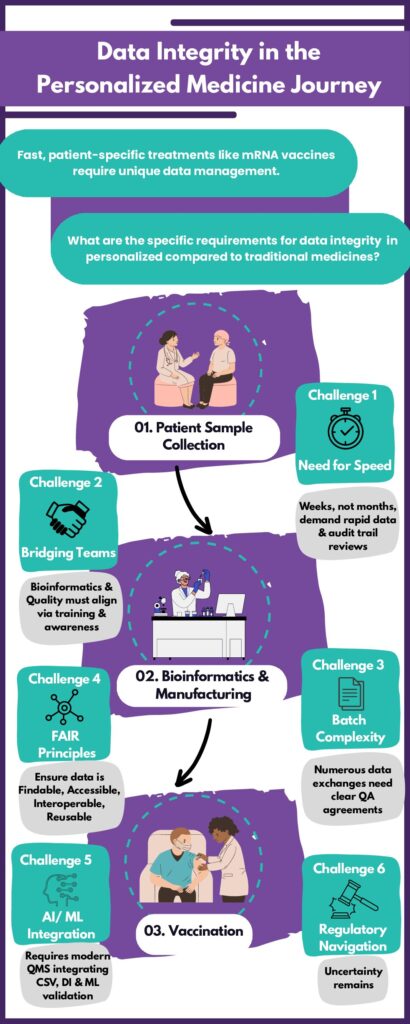
What are the specific requirements for DI and Data Governance in personalized medicine compared to traditional pharmaceuticals?
1. In mRNA technology, short throughput times—just weeks from sample collection to vaccination — demand rapid and thorough data review. Risk-based data and audit trail reviews must account for this urgency.
2. Bioinformatics and quality teams must collaborate despite differing backgrounds. Regular training and awareness campaigns are key to ensuring compliance and shared understanding.
3. Each patient represents one batch, with the product moving from bedside to bench and back, involving many data exchanges. Clear quality assurance agreements must define Data Management expectations and error handling.
4. Data must follow the FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable) principles to prevent OOS (Out of Specification) and deviations—critical for patients.
5. Machine Learning (ML) may enhance personalization requiring a modern Quality Management system integrating CSV, Data Integrity, and ML validation.
6. Regulatory uncertainty remains, especially in upstream processes—from biology to in-silico models. Organizations should define critical process steps (ICH Q8), map Critical Quality Attributes (CQA) and apply Quality Risk Management (ICH Q9).